publications
My works have been published in top-tier computer vision, machine learning, and robotics conferences and journals such as NeurIPS, ICRA, IROS, and RA-L.
2025
- ICCV
 GARF: Learning Generalizable 3D Reassembly for Real-World FracturesSihang Li, Jiang Zeyu, Chen Grace, and 9 more authorsInternational Conference on Computer Vision, 2025
GARF: Learning Generalizable 3D Reassembly for Real-World FracturesSihang Li, Jiang Zeyu, Chen Grace, and 9 more authorsInternational Conference on Computer Vision, 20253D reassembly is a challenging spatial intelligence task with broad applications across scientific domains. While large-scale synthetic datasets have fueled promising learning-based approaches, their generalizability to different domains is limited. Critically, it remains uncertain whether models trained on synthetic datasets can generalize to real-world fractures where breakage patterns are more complex. To bridge this gap, we propose GARF, a generalizable 3D reassembly framework for real-world fractures. GARF leverages fracture-aware pretraining to learn fracture features from individual fragments, with flow matching enabling precise 6-DoF alignments. At inference time, we introduce one-step preassembly, improving robustness to unseen objects and varying numbers of fractures. In collaboration with archaeologists, paleoanthropologists, and ornithologists, we curate Fractura, a diverse dataset for vision and learning communities, featuring real-world fracture types across ceramics, bones, eggshells, and lithics. Comprehensive experiments have shown our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets, achieving 82.87% lower rotation error and 25.15% higher part accuracy. This sheds light on training on synthetic data to advance real-world 3D puzzle solving, demonstrating its strong generalization across unseen object shapes and diverse fracture types.
- ICCV
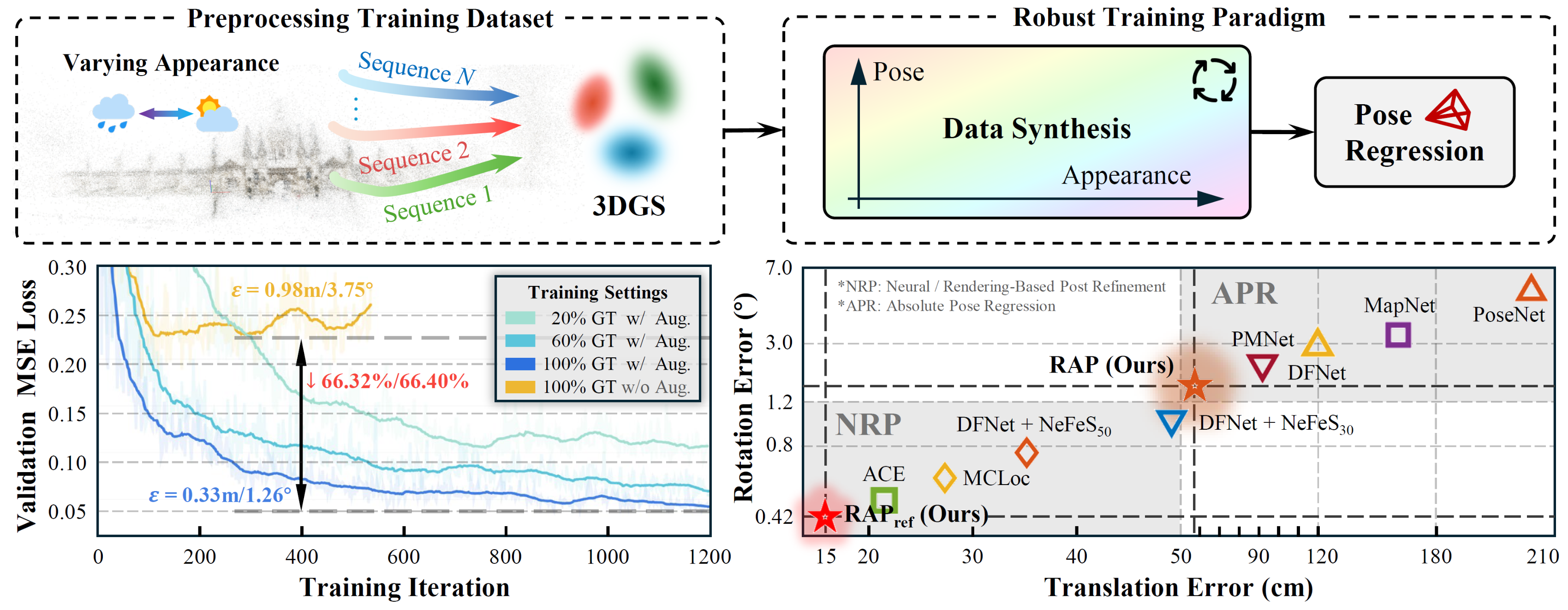 Adversarial Exploitation of Data Diversity Improves Visual LocalizationSihang Li, Siqi Tan, Bowen Chang, and 3 more authorsInternational Conference on Computer Vision, 2025
Adversarial Exploitation of Data Diversity Improves Visual LocalizationSihang Li, Siqi Tan, Bowen Chang, and 3 more authorsInternational Conference on Computer Vision, 2025Visual localization, which estimates a camera’s pose within a known scene, is a long-standing challenge in vision and robotics. Recent end-to-end methods that directly regress camera poses from query images have gained attention for fast inference. However, existing methods often struggle to generalize to unseen views. In this work, we aim to unleash the power of data synthesis to promote the generalizability of pose regression. Specifically, we lift real 2D images into 3D Gaussian Splats with varying appearance and deblurring abilities, which are then used as a data engine to synthesize more posed images. To fully leverage the synthetic data, we build a two-branch joint training pipeline, with an adversarial discriminator to bridge the syn-to-real gap. Experiments on established benchmarks show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art end-to-end approaches, reducing translation and rotation errors by 50% and 21.6% on indoor datasets, and 35.56% and 38.7% on outdoor datasets. We also validate the effectiveness of our method in dynamic driving scenarios under varying weather conditions. Notably, as data synthesis scales up, our method exhibits a growing ability to interpolate and extrapolate training data for localizing unseen views.
2024
- NeurIPS
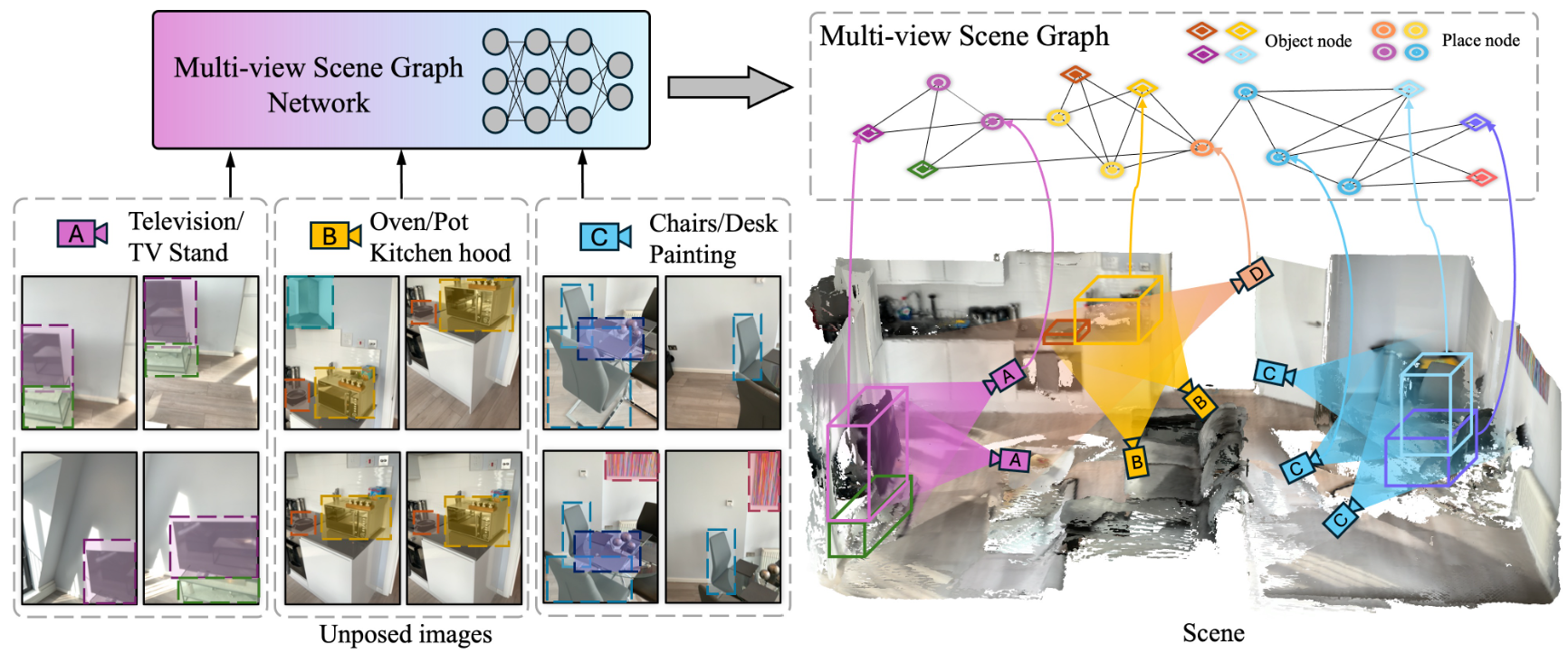 Multiview Scene GraphJuexiao Zhang, Gao Zhu, Sihang Li, and 4 more authorsIn Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2024
Multiview Scene GraphJuexiao Zhang, Gao Zhu, Sihang Li, and 4 more authorsIn Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2024A proper scene representation is central to the pursuit of spatial intelligence where agents can robustly reconstruct and efficiently understand 3D scenes. A scene representation is either metric, such as landmark maps in 3D reconstruction, 3D bounding boxes in object detection, or voxel grids in occupancy prediction, or topological, such as pose graphs with loop closures in SLAM or visibility graphs in SfM. In this work, we propose to build \textitMultiview Scene Graphs (MSG) from unposed images, representing a scene topologically with interconnected place and object nodes. The task of building MSG is challenging for existing representation learning methods since it needs to jointly address both visual place recognition, object detection, and object association from images with limited fields of view and potentially large viewpoint changes. To evaluate any method tackling this task, we developed an MSG dataset and annotation based on a public 3D dataset. We also propose an evaluation metric based on the intersection-over-union score of MSG edges. Moreover, we develop a novel baseline method built on mainstream pretrained vision models, combining visual place recognition and object association into one Transformer decoder architecture. Experiments demonstrate our method has superior performance compared to existing relevant baselines.
- IROS
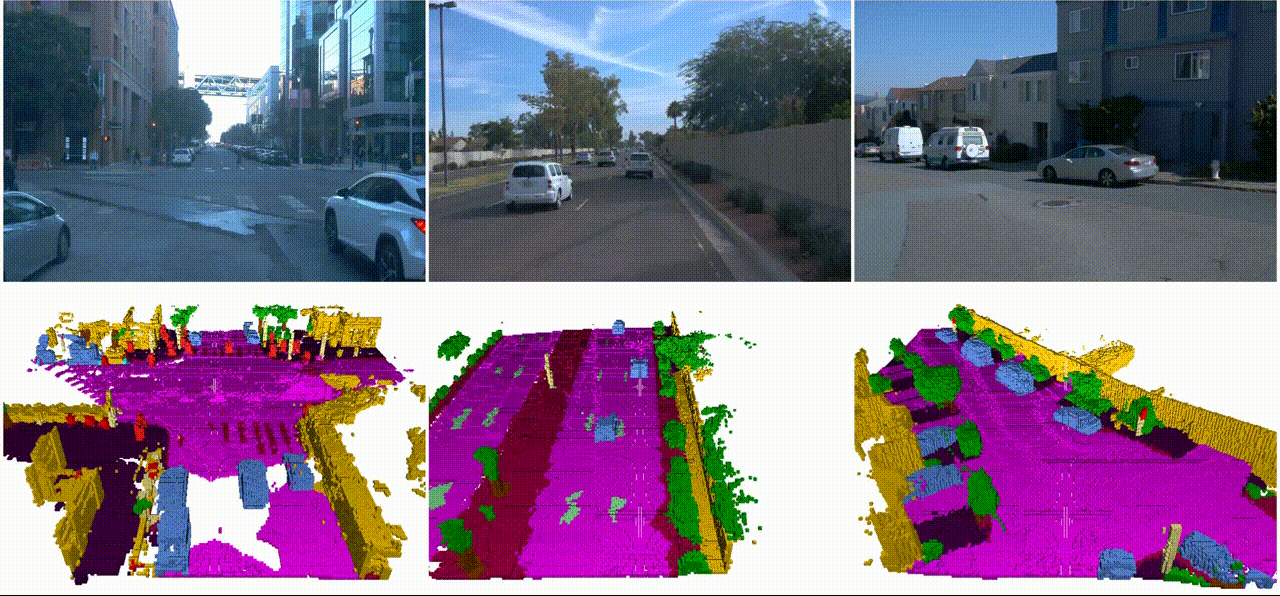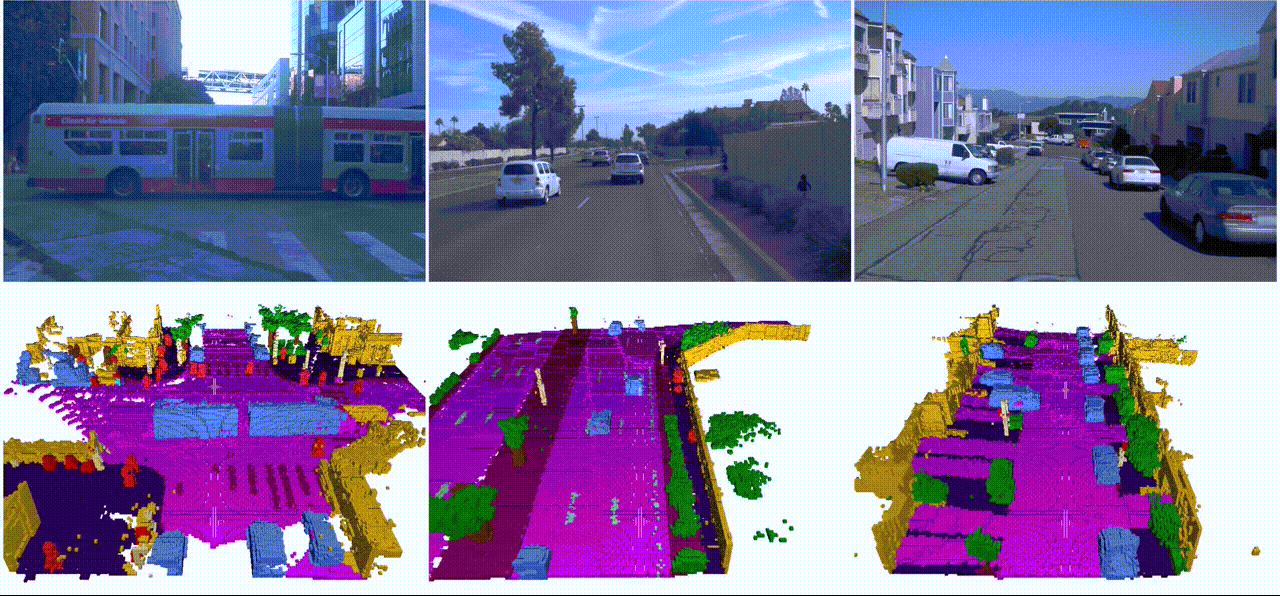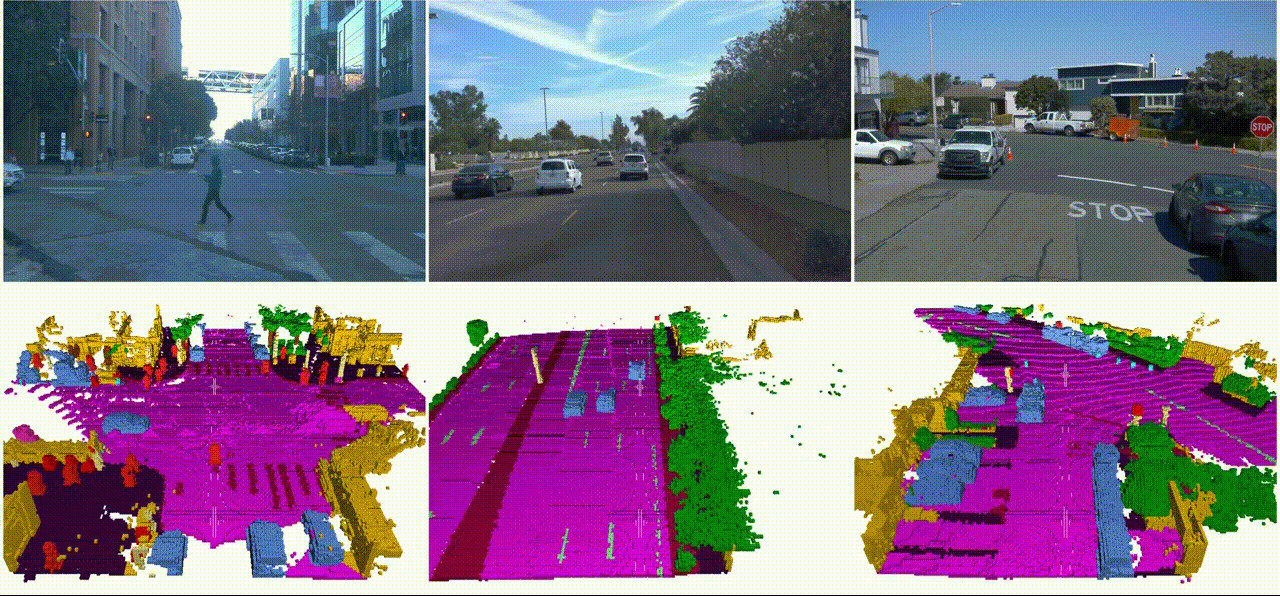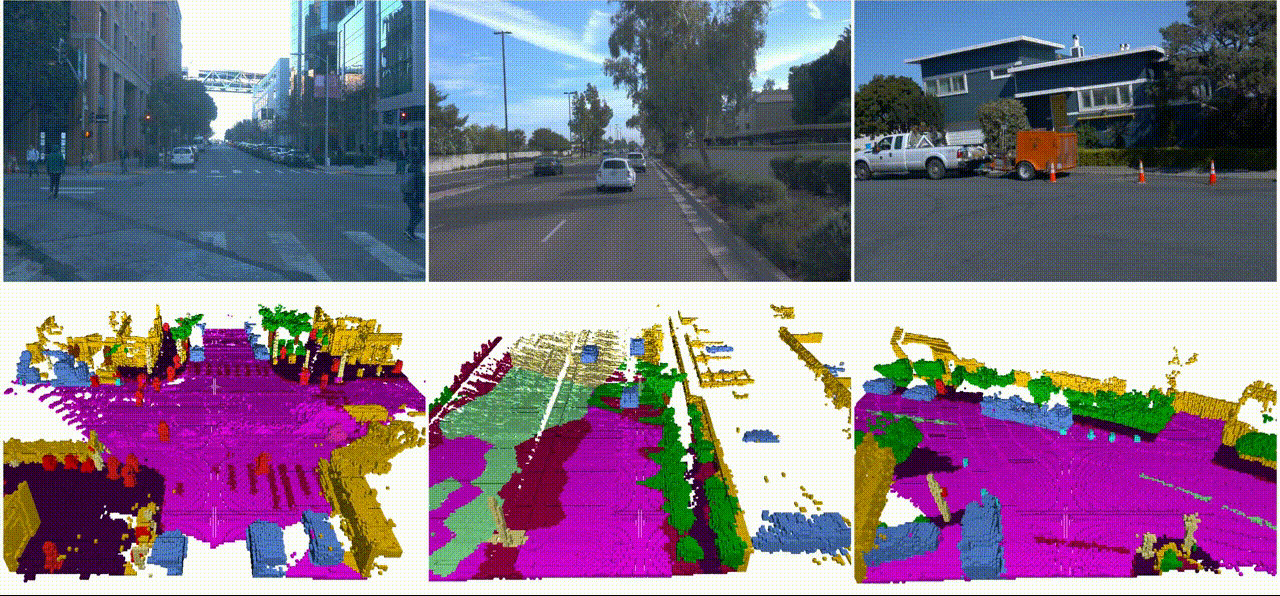 SSCBench: A Large-Scale 3D Semantic Scene Completion Benchmark for Autonomous DrivingYiming Li, Sihang Li, Xinhao Liu, and 8 more authorsIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2024
SSCBench: A Large-Scale 3D Semantic Scene Completion Benchmark for Autonomous DrivingYiming Li, Sihang Li, Xinhao Liu, and 8 more authorsIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2024Semantic scene completion (SSC) is crucial for holistic 3D scene understanding by jointly estimating semantics and geometry from sparse observations. However, progress in SSC, particularly in autonomous driving scenarios, is hindered by the scarcity of high-quality datasets. To overcome this challenge, we introduce SSCBench, a comprehensive benchmark that integrates scenes from widely-used automotive datasets (e.g., KITTI-360, nuScenes, and Waymo). SSCBench follows an established setup and format in the community, facilitating the easy exploration of the camera- and LiDAR-based SSC across various real-world scenarios. We present quantitative and qualitative evaluations of state-of-the-art algorithms on SSCBench and commit to continuously incorporating novel automotive datasets and SSC algorithms to drive further advancements in this field.
2023
- IROS
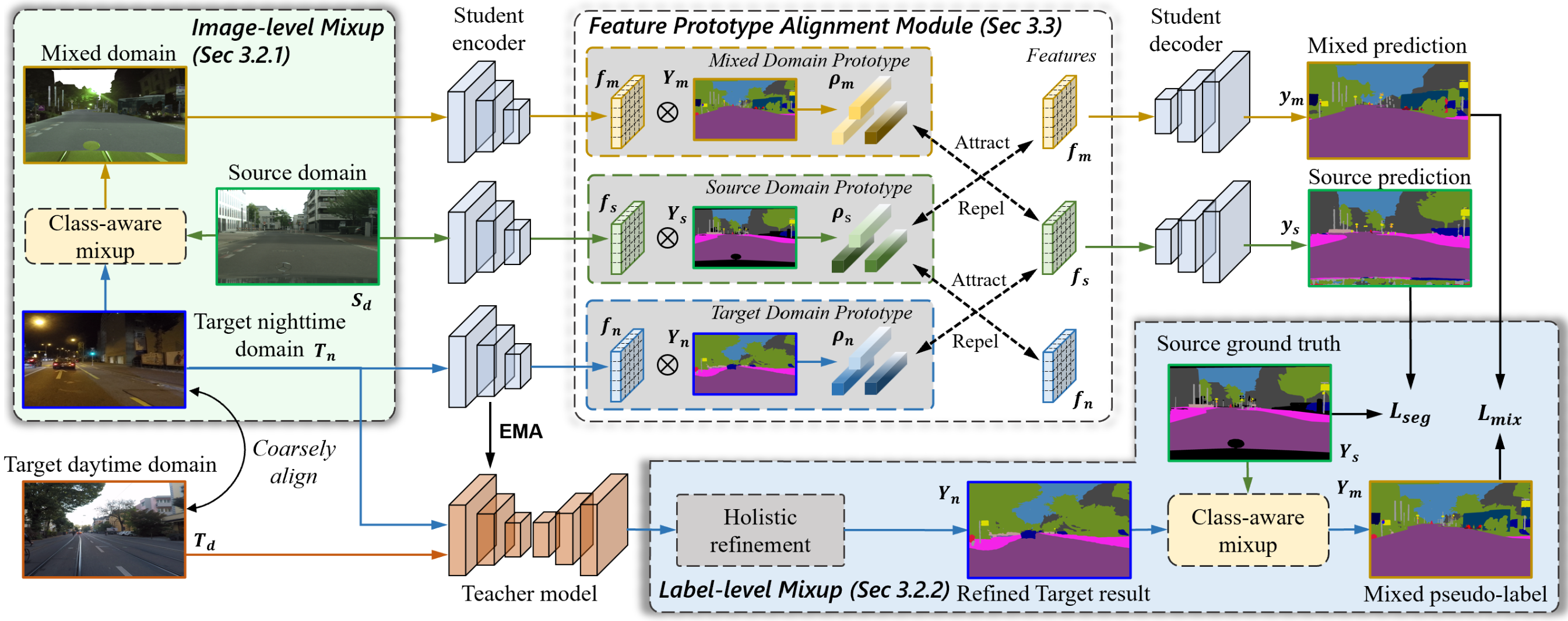 Towards Dynamic and Small Objects Refinement for Unsupervised Domain Adaptative Nighttime Semantic SegmentationJingyi Pan, Sihang Li, Yucheng Chen, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2023
Towards Dynamic and Small Objects Refinement for Unsupervised Domain Adaptative Nighttime Semantic SegmentationJingyi Pan, Sihang Li, Yucheng Chen, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2023Nighttime semantic segmentation is essential for various applications, \eg, autonomous driving, which often faces challenges due to poor illumination and the lack of well-annotated datasets. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) has shown potential for addressing the challenges and achieved remarkable results for nighttime semantic segmentation. However, existing methods still face limitations in 1) their reliance on style transfer or relighting models, which struggle to generalize to complex nighttime environments, and 2) their ignorance of dynamic and small objects like vehicles and traffic signs, which are difficult to be directly learned from other domains. This paper proposes a novel UDA method that refines both label and feature levels for dynamic and small objects for nighttime semantic segmentation. First, we propose a dynamic and small object refinement module to complement the knowledge of dynamic and small objects that are normally context-inconsistent due to poor illumination. Then, we design a feature prototype alignment module to reduce the domain gap by deploying contrastive learning between features and prototypes of the same class from different domains, while re-weighting the categories of dynamic and small objects. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms prior arts by a large margin for nighttime segmentation. Our codes will be released soon.
- RA-L
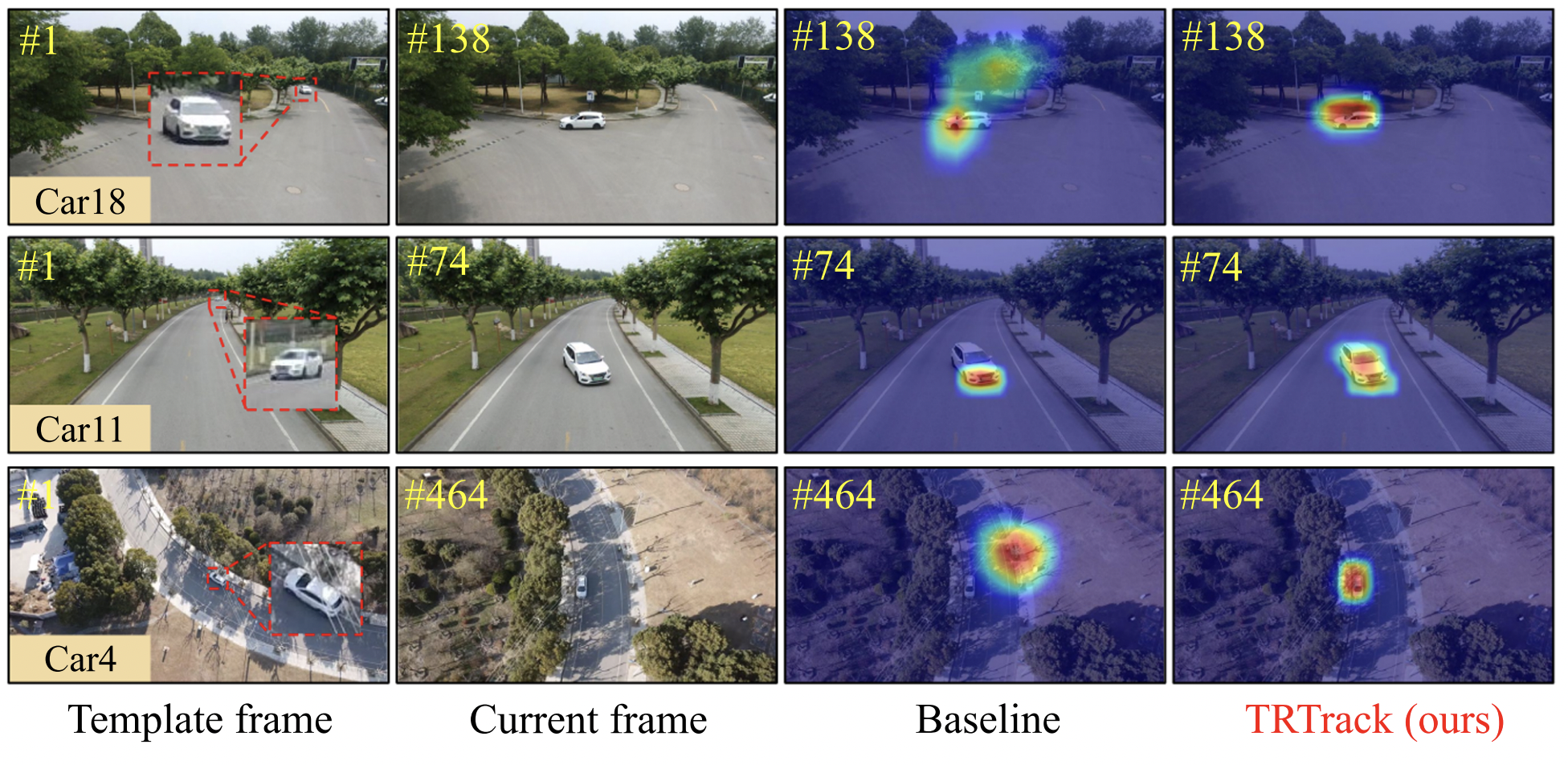 Boosting UAV Tracking with Voxel-based Trajectory-Aware Pre-TrainingIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023
Boosting UAV Tracking with Voxel-based Trajectory-Aware Pre-TrainingIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023Siamese network-based object tracking has remarkably promoted the automatic capability for highlymaneuvered unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). However, the leading-edge tracking framework often depends on template matching, making it trapped when facing multiple views of object in consecutive frames. Moreover, the general imagelevel pretrained backbone can overfit to holistic representations, causing the misalignment to learn object-level properties in UAV tracking. To tackle these issues, this work presents TRTrack, a comprehensive framework to fully exploit the stereoscopic representation for UAV tracking. Specifically, a novel pretraining paradigm method is proposed. Through trajectoryaware reconstruction training, the capability of the backbone to extract stereoscopic structure feature is strengthened without any parameter increment. Accordingly, an innovative hierarchical self-attention Transformer is proposed to capture the local detail information and global structure knowledge. For optimizing the correlation map, we proposed a novel spatial correlation refinement (SCR) module, which promotes the capability of modeling the long-range spatial dependencies. Comprehensive experiments on three UAV challenging benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed TRTrack achieves superior UAV tracking performance in both precision and efficiency. Quantitative tests in real-world settings fully prove the effectiveness of our work.
- RA-L
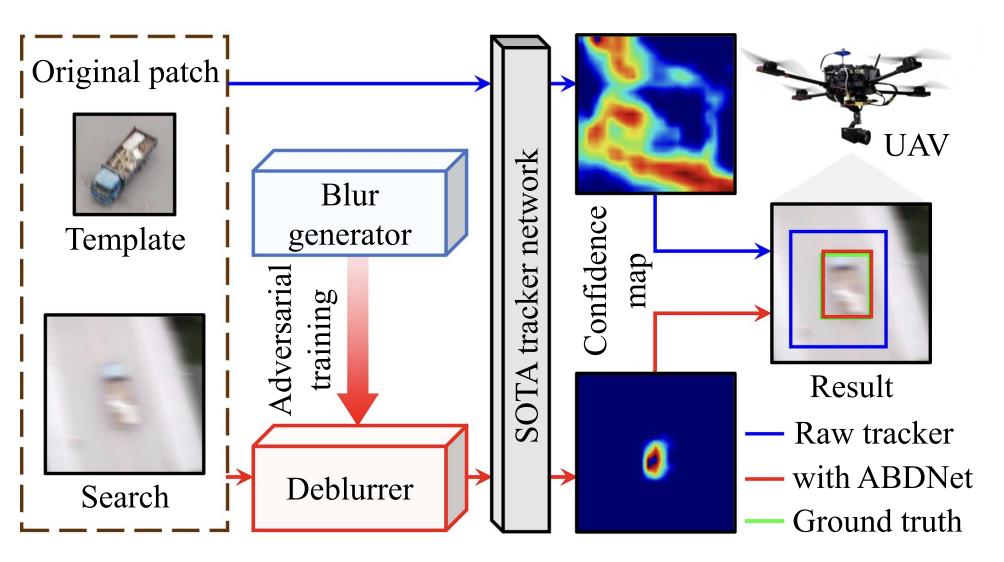 Adversarial Blur-Deblur Network for Robust UAV TrackingIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023
Adversarial Blur-Deblur Network for Robust UAV TrackingIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking has been widely applied in real-world applications such as surveillance and monitoring. However, the inherent high maneuverability and agility of UAV often lead to motion blur, which can impair the visual appearance of the target object and easily degrade the existing trackers. To overcome this challenge, this work proposes a tracking-oriented adversarial blur-deblur network (ABDNet), composed of a novel deblurrer to recover the visual appearance of the tracked object, and a brand-new blur generator to produce realistic blurry images for adversarial training. More specifically, the deblurrer progressively refines the features through pixel-wise, spatial-wise, and channel-wise stages to achieve excellent deblurring performance. The blur generator adaptively fuses an image sequence with a learnable kernel to create realistic blurry images. During training, ABDNet is plugged into the state-of-the-art real-time trackers and trained with blurring-deblurring loss as well as tracking loss. During inference, the blur generator is removed, while the deblurrer and the tracker can work together for UAV tracking. Extensive experiments in both public datasets and real-world testing have validated the effectiveness of ABDNet.
- ICRA
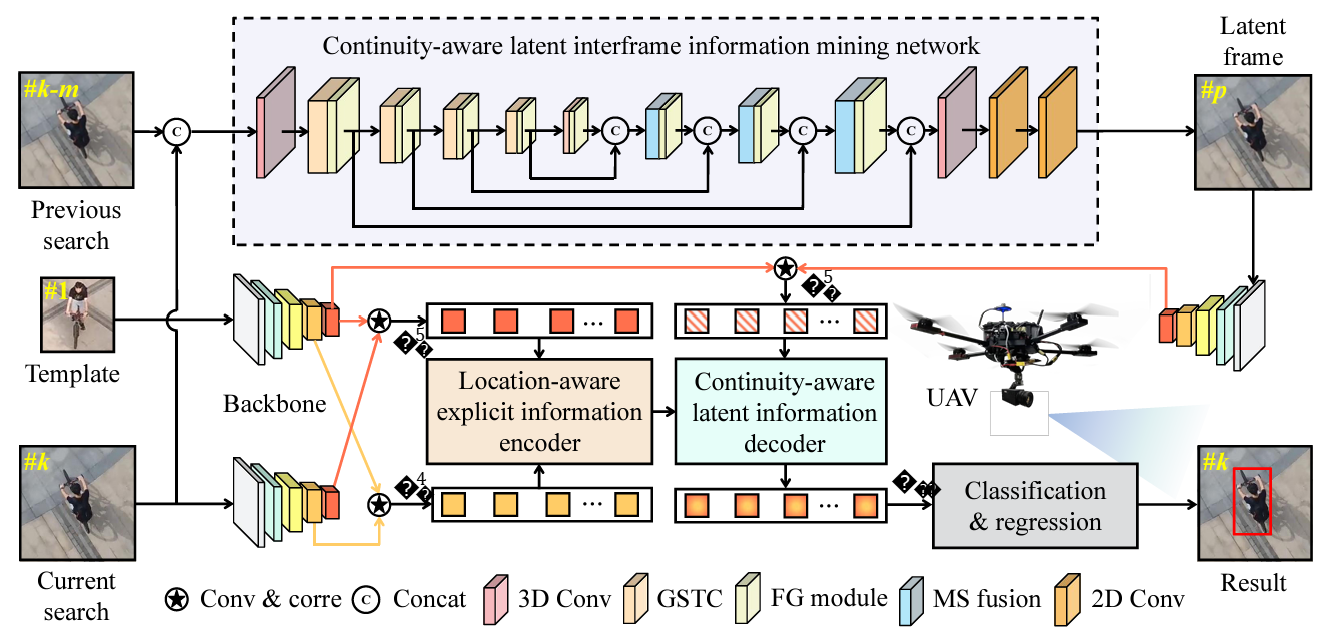 Continuity-aware latent interframe information mining for reliable UAV trackingChanghong Fu, Mutian Cai, Sihang Li, and 3 more authorsIn IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2023
Continuity-aware latent interframe information mining for reliable UAV trackingChanghong Fu, Mutian Cai, Sihang Li, and 3 more authorsIn IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2023Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking is crucial for autonomous navigation and has broad applications in robotic automation fields. However, reliable UAV tracking remains a challenging task due to various difficulties like frequent occlusion and aspect ratio change. Additionally, most of the existing work mainly focuses on explicit information to improve tracking performance, ignoring potential interframe connections. To address the above issues, this work proposes a novel framework with continuity-aware latent interframe information mining for reliable UAV tracking, i.e., ClimRT. Specifically, a new efficient continuity-aware latent interframe information mining network (ClimNet) is proposed for UAV tracking, which can generate highly-effective latent frame between two adjacent frames. Besides, a novel location-continuity Transformer (LCT) is designed to fully explore continuity-aware spatial-temporal information, thereby markedly enhancing UAV tracking. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on three authoritative aerial benchmarks strongly validate the robustness and reliability of ClimRT in UAV tracking performance. Furthermore, real-world tests on the aerial platform validate its practicability and effectiveness.
- ICRA
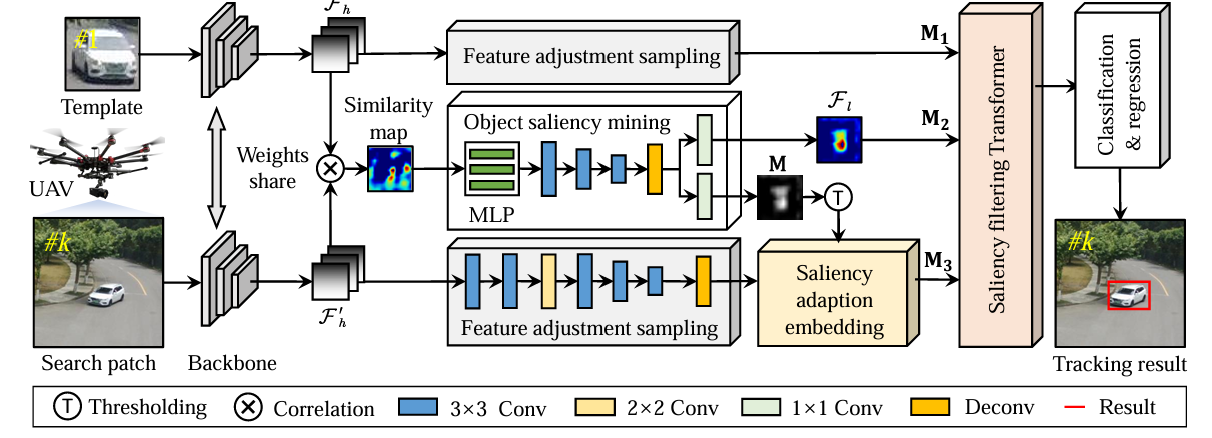 SGDViT: saliency-guided dynamic vision transformer for UAV trackingLiangliang Yao, Changhong Fu, Sihang Li, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2023
SGDViT: saliency-guided dynamic vision transformer for UAV trackingLiangliang Yao, Changhong Fu, Sihang Li, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2023Vision-based object tracking has boosted extensive autonomous applications for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). However, the dynamic changes in flight maneuver and viewpoint encountered in UAV tracking pose significant difficulties, e.g. , aspect ratio change, and scale variation. The conventional cross-correlation operation, while commonly used, has limitations in effectively capturing perceptual similarity and incorporates extraneous background information. To mitigate these limitations, this work presents a novel saliency-guided dynamic vision Transformer (SGDViT) for UAV tracking. The proposed method designs a new task-specific object saliency mining network to refine the cross-correlation operation and effectively discriminate foreground and background information. Additionally, a saliency adaptation embedding operation dynamically generates tokens based on initial saliency, thereby reducing the computational complexity of the Transformer architecture. Finally, a lightweight saliency filtering Transformer further refines saliency information and increases the focus on appearance information. The efficacy and robustness of the proposed approach have been thoroughly assessed through experiments on three widely-used UAV tracking benchmarks and real-world scenarios, with results demonstrating its superiority.
2022
- IROS
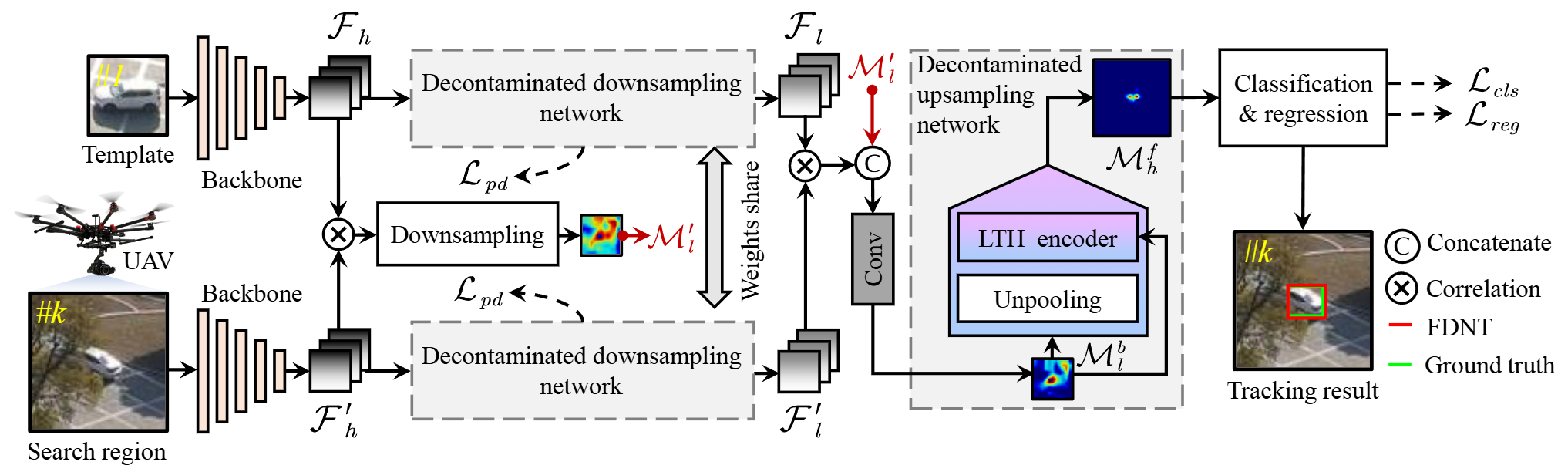 End-to-end feature decontaminated network for UAV trackingIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2022
End-to-end feature decontaminated network for UAV trackingIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2022Object feature pollution is one of the burning issues in vision-based UAV tracking, commonly caused by occlusion, fast motion, and illumination variation. Due to the contaminated information in the polluted object features, most trackers fail to precisely estimate the object location and scale. To address the above disturbing issue, this work proposes a novel end-to-end feature decontaminated network for efficient and effective UAV tracking, i.e., FDNT. FDNT mainly includes two modules: a decontaminated downsampling network and a decontaminated upsampling network. The former reduces the interference information of the feature pollution and enhanced the expression of the object location information with two asymmetric convolution branches. The latter restores the object scale information with the super-resolution technology-based low-to-high encoder, achieving a further decontamination effect. Moreover, a novel pooling distance loss is carefully developed to assist the decontaminated downsampling network in concentrating on the critical regions with the object information. Exhaustive experiments on three well-known benchmarks validate the effectiveness of FDNT, especially on the sequences with feature pollution. In addition, real-world tests show the efficiency of FDNT with 31.4 frames per second.
- IROS
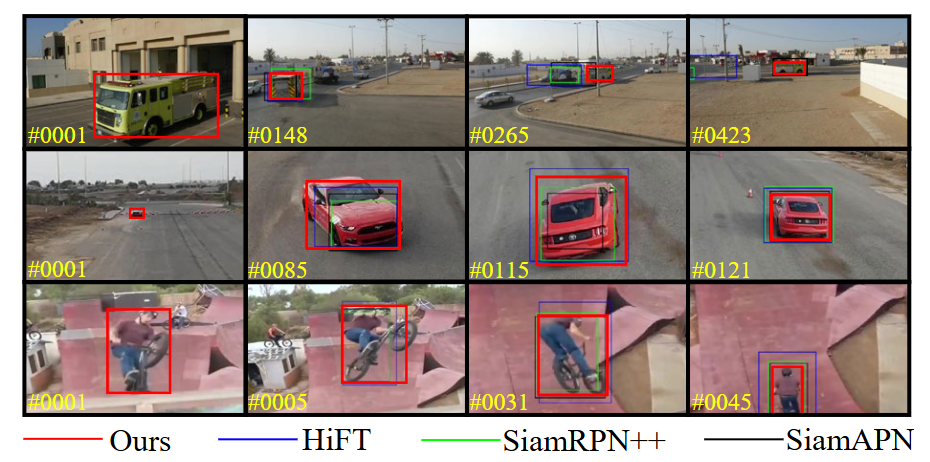 Local perception-aware transformer for aerial trackingChanghong Fu, Weiyu Peng, Sihang Li, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2022
Local perception-aware transformer for aerial trackingChanghong Fu, Weiyu Peng, Sihang Li, and 2 more authorsIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2022Transformer-based visual object tracking has been utilized extensively. However, the Transformer structure is lack of enough inductive bias. In addition, only focusing on encoding the global feature does harm to modeling local details, which restricts the capability of tracking in aerial robots. Specifically, with local-modeling to global-search mechanism, the proposed tracker replaces the global encoder by a novel local-recognition encoder. In the employed encoder, a localrecognition attention and a local element correction network are carefully designed for reducing the global redundant information interference and increasing local inductive bias. Meanwhile, the latter can model local object details precisely under aerial view through detail-inquiry net. The proposed method achieves competitive accuracy and robustness in several authoritative aerial benchmarks with 316 sequences in total. The proposed tracker’s practicability and efficiency have been validated by the real-world tests.
- IROS
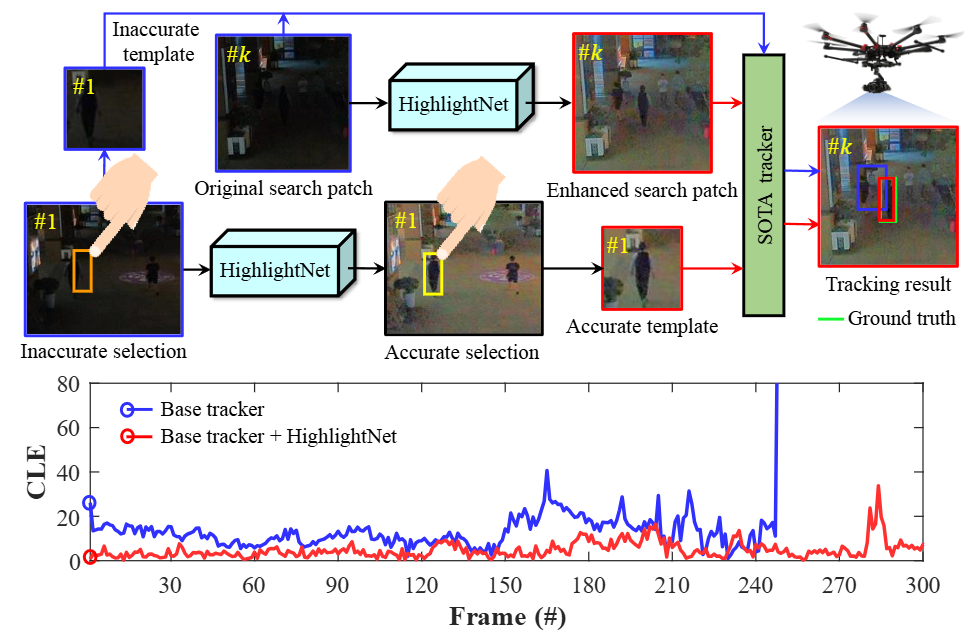 HighlightNet: highlighting low-light potential features for real-time UAV trackingIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2022
HighlightNet: highlighting low-light potential features for real-time UAV trackingIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2022Low-light environments have posed a formidable challenge for robust unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking even with state-of-the-art (SOTA) trackers since the potential image features are hard to extract under adverse light conditions. Besides, due to the low visibility, accurate online selection of the object also becomes extremely difficult for human monitors to initialize UAV tracking in ground control stations. To solve these problems, this work proposes a novel enhancer, i.e., HighlightNet, to light up potential objects for both human operators and UAV trackers. By employing Transformer, HighlightNet can adjust enhancement parameters according to global features and is thus adaptive for the illumination variation. Pixel-level range mask is introduced to make HighlightNet more focused on the enhancement of the tracking object and regions without light sources. Furthermore, a soft truncation mechanism is built to prevent background noise from being mistaken for crucial features. Evaluations on image enhancement benchmarks demonstrate HighlightNet has advantages in facilitating human perception. Experiments on the public UAVDark135 benchmark show that HightlightNet is more suitable for UAV tracking tasks than other state-of-theart (SOTA) low-light enhancers. In addition, real-world tests on a typical UAV platform verify HightlightNet’s practicability and efficiency in nighttime aerial tracking-related applications.
- ICRA
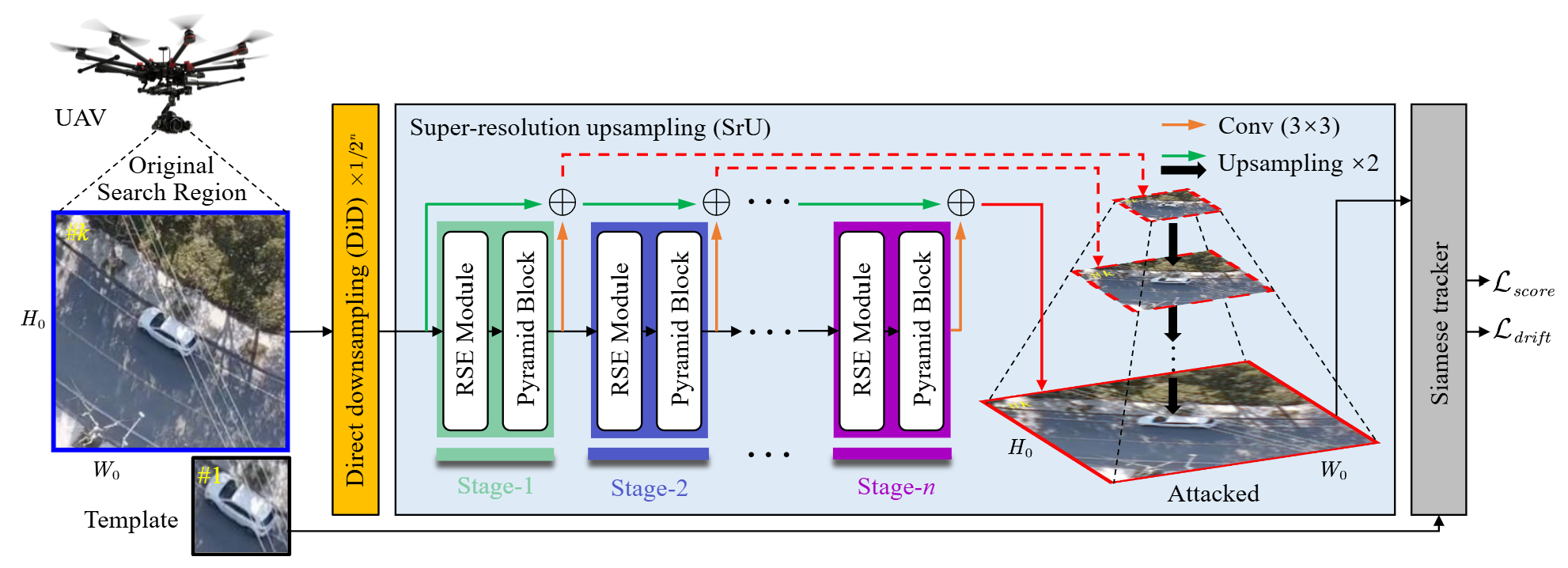 Ad 2 attack: Adaptive adversarial attack on real-time uav trackingChanghong Fu, Sihang Li, Xinnan Yuan, and 3 more authorsIn International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2022
Ad 2 attack: Adaptive adversarial attack on real-time uav trackingChanghong Fu, Sihang Li, Xinnan Yuan, and 3 more authorsIn International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2022Visual tracking is adopted to extensive unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-related applications, which leads to a highly demanding requirement on the robustness of UAV trackers. However, adding imperceptible perturbations can easily fool the tracker and cause tracking failures. This risk is often overlooked and rarely researched at present. Therefore, to help increase awareness of the potential risk and the robustness of UAV tracking, this work proposes a novel adaptive adversarial attack approach, i.e., Ad2Attack, against UAV object tracking. Specifically, adversarial examples are generated online during the resampling of the search patch image, which leads trackers to lose the target in the following frames. Ad2Attack is composed of a direct downsampling module and a super-resolution upsampling module with adaptive stages. A novel optimization function is proposed for balancing the imperceptibility and efficiency of the attack. Comprehensive experiments on several well-known benchmarks and real-world conditions show the effectiveness of our attack method, which dramatically reduces the performance of the most advanced Siamese trackers.